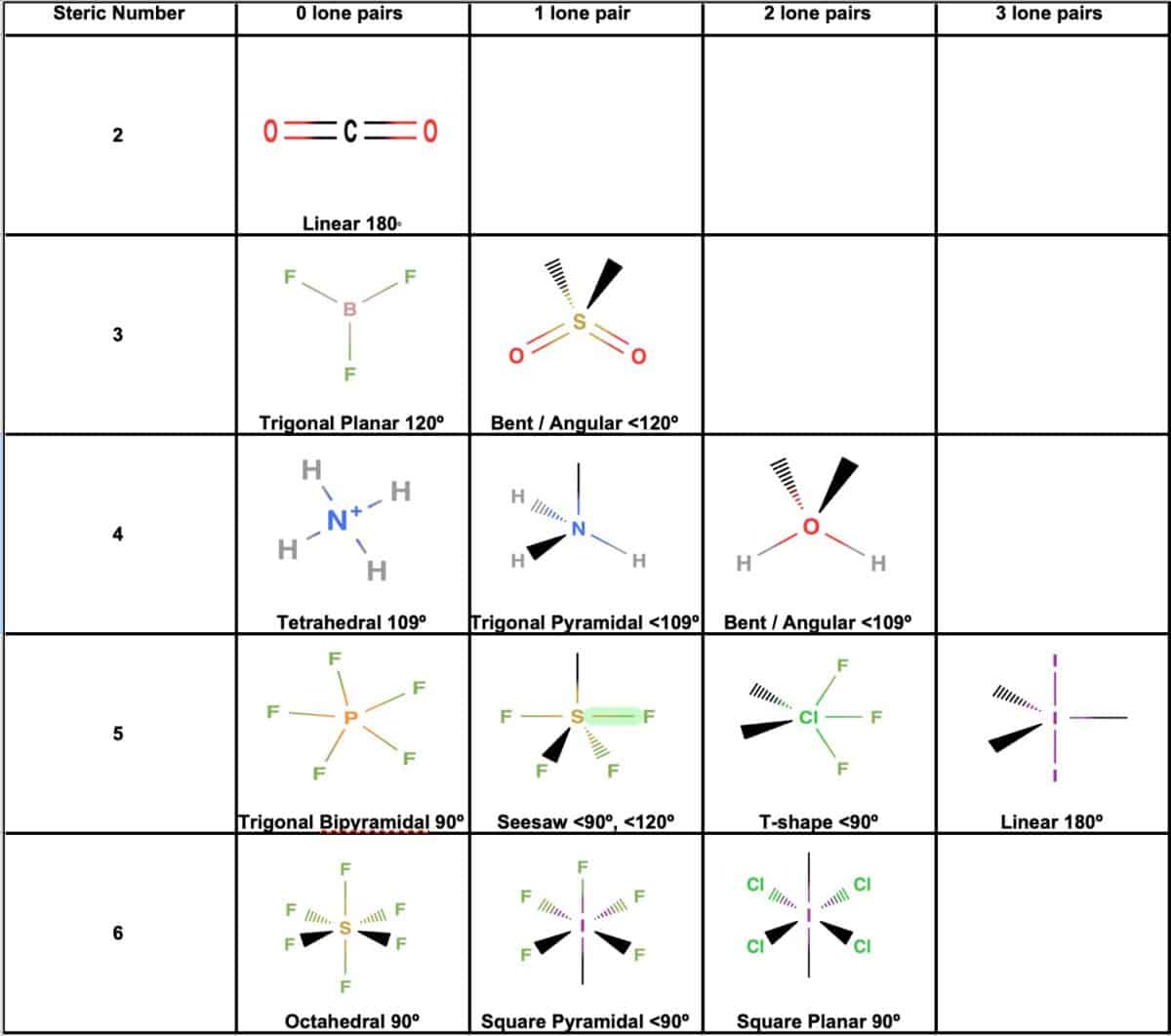
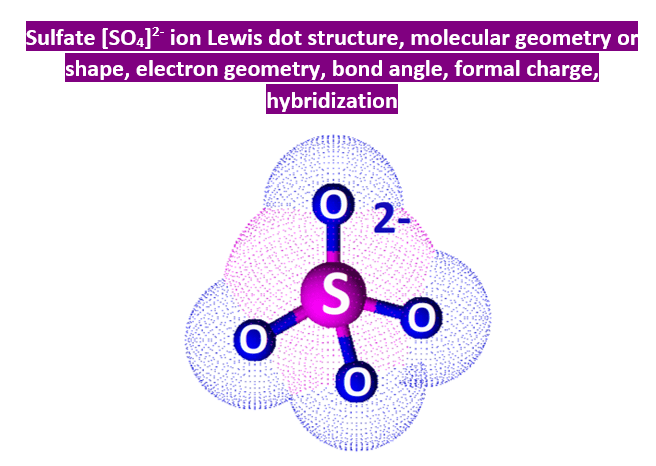
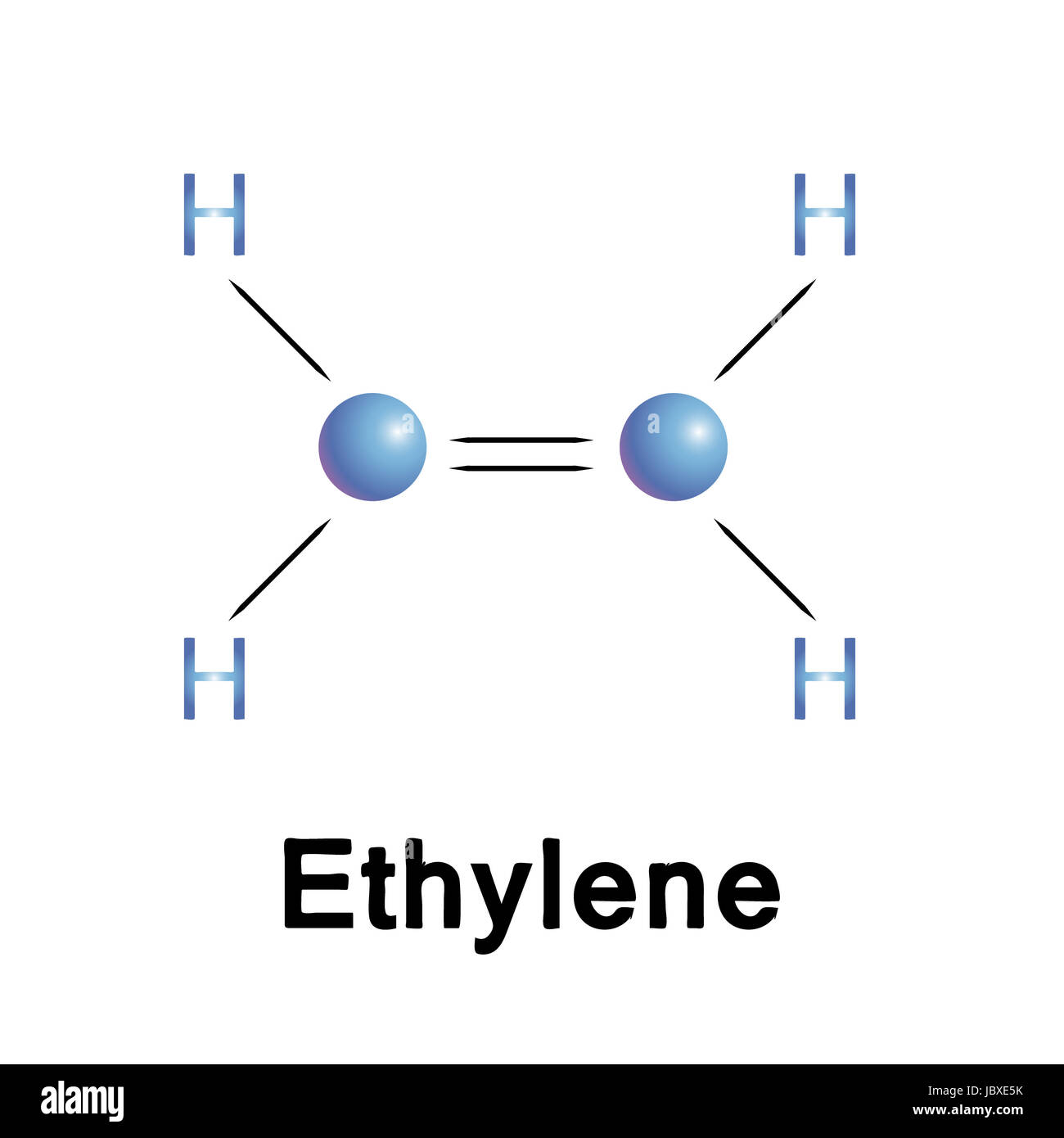
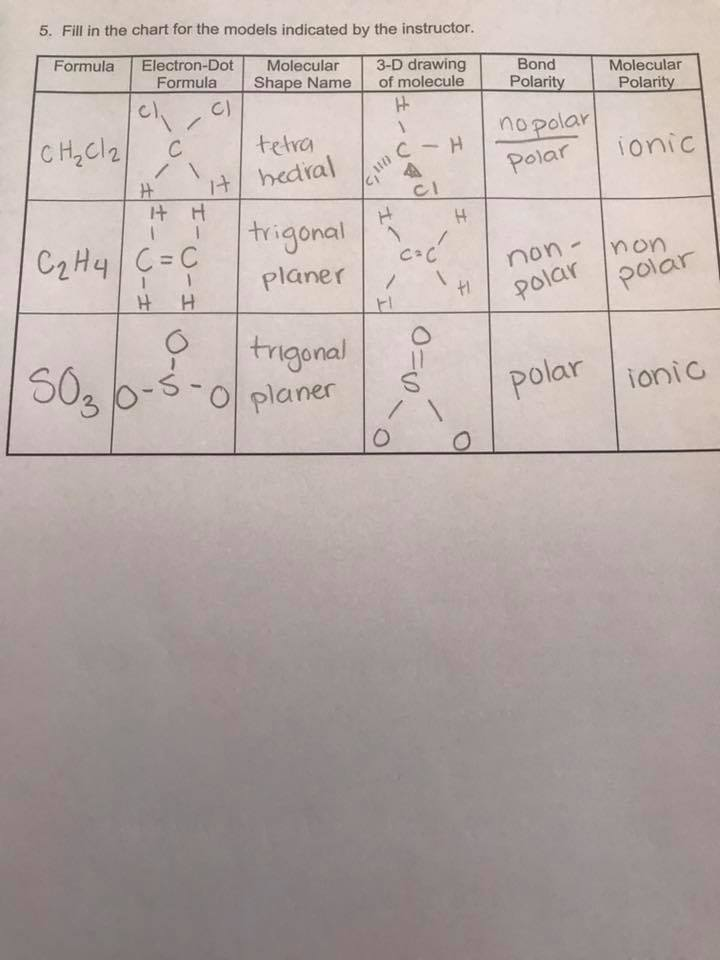
(methene = 28. 05 kg/kmol). Consider the equilibrium c2h6 (g) ⇌ c2h4 (g) + h2 (g). · master the c2h4 lewis structure with our step-by-step guide and detailed diagram. Learn how to draw the ethylene molecule, understand its electron geometry, and explore its molecular shape. Basic properties and structure of ethylene ethylene is a hydrocarbon, specifically an alkene, represented by the chemical formula c 2 h 4. Lhv=47260 kj/kg} (15) your solution’s ready to go! Consider the representation of dashed lines in the orbital structure of ethene, c2h4, as they typically signify a type of bond formation involving unhybridized p-orbitals. The point group of ethene, c2h4, is d 2h. · each carbon atom has sp2 hybridization and are locked in the same plane due to the double bond located between them. determine the higher and lower heating values. Despite being a simple molecule, its unique properties and versatility make it invaluable. It is generally believed that diamonds last forever. This reaction is ________. Express the free energy change in joules to four significant figures. For the reaction c2h6 (g) → c2h4 (g) + h2 (g) δh° is +137 kj/mol and δs° is +120 j/k ∙ mol. Draw the lewis structures of c2h6, c2h4, and c2h2. draw the molecules by placing atoms on the grid and connecting them with bonds. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. Consider the following reaction: Include all hydrogen atoms. Draw the lewis structure for the ethylene (c2h4 molecule. A deep dive into planar structure ethylene, also known as ethene (c₂h₄), is a simple yet fascinating hydrocarbon with a distinct geometric shape that plays a crucial role in its chemical properties and reactivity. This comprehensive tutorial covers bond formation, hybridization, and resonance, making it essential for chemistry students and enthusiasts studying organic … A) spontaneous at all temperatures b) spontaneous only at high temperature c) spontaneous only at low temperature d) nonspontaneous at all temperatures Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy-to-learn solution you can count on. Understanding its molecular geometry is key to grasping its behavior in various chemical reactions and … · 💡 the c2h4 lewis structure is an important concept in organic chemistry, as it helps us understand the bonding and geometry of molecules. C2h4( g)+h2( g)→c2h6( g) δh =−137. 5 kj;δs =−120. 5 j/k calculate δg at 25∘c and determine whether the reaction is spontaneous. The coordinate axes and the molecular structure are shown in figure 3. Label the structure of c2h4, including overlapping orbitals, and label all bonds. At 1000 k and a constant total pressure of 1 bar, c2h6 (g) is introduced into a reaction vessel. We intend to construct symmetry adapted linear combinations (salcs) of atomic … Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Elemental carbon usually exists in one of two forms: Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. label the structure of c2h6, including overlapping orbitals, and label all bonds. The carbon atoms have 3 electron groups surrounding them with no lone pairs present thefore, it will have a trigonal planar geometry The enthalpy of formation of ethene, c2h4, at 1 atm, 25\deg c is 52,280 kj/kmol. Assume all bond angles are 120 degree. The double bond between the carbon atoms is a key feature of the molecule, and it plays a crucial role in many chemical reactions, including addition reactions and polymerization reactions. · unveiling the geometry of ethylene (c₂h₄): Graphite or diamond.
C2H4 Molecular Geometry: The Properties That Make It So Useful (And Dangerous!)
(methene = 28. 05 kg/kmol). Consider the equilibrium c2h6 (g) ⇌ c2h4 (g) + h2 (g). · master the c2h4 lewis structure with our step-by-step...